The realm of translation is massive, with influence in every industry and relevance in every language. It connects us in a globalized world, allowing people worldwide to share art, music, and literature. It allows businesses to expand internationally and overcome language barriers that previously kept different cultures separate.
With such a broad reach, it’s reasonable that there are multiple ways to translate content from one language to another. Traditional translation, localization, and transcreation are all different ways to do so, and while they all sound similar, they have several key differences that differentiate them:
What is Translation?
To understand transcreation and localization, you first need to understand translation. Translation is a process that changes content from one language into another language. During translation, a linguist with expertise in multiple languages replaces words and recreates phrases from the source language into the target language. However, translation isn’t just swapping words for an alternate-language counterpart: it involves rewriting phrases and sentences to stay grammatically correct in both languages and including or changing contexts to ensure audiences in the target language understand the content.
What are the Types of Translation?
There are many different types of translation, which vary from the complexity of the translation to the field that the translation is for.
What are the Three Types of Translation?
Generally, there are three different levels of translation, which are measured based on the project’s complexity:
- Literal Translation: Literal translations are direct, nearly one-to-one translations of the source text. They aim to replicate the source material as closely as possible, sometimes at the expense of the reader’s understanding of cultural context. Literal translations are best for scientific, legal, medical, or academic translations using exact, field-specific terminology.
- Interpretative Translation: Interpretative translations aren’t as exact as literal translations, but they still aim to convey complex concepts and ideas as closely as possible. Interpretative translations are best for technical projects, like safety manuals, instructions, or educational resources, because translators can alter specific terms or common phrases to fit a target language’s memetics.
- Free Translation: Free translations are the least exact of the three types, as they aim to convey tone and emotional concepts over exact words. Free translations are best for translating creative content, where audience understanding is paramount.
The Main Types of Translation
There are also different types of translation, which vary depending on the industries they work with. These different translation types may also use specific levels of translation as well:
- Creative Translation: Creative Translation involves translating any and all creative materials. Books, movies, video games, and other visual media are probably the most well-known subjects of creative translation. But this field also includes marketing materials, like packaging labels, iconography, web copy, SEO keywords, and other aspects of marketing translation.
- Corporate Translation: This type of translation revolves around translating for businesses. While it’s true that businesses do need marketing translation services, they also need things like employee manuals, customer-facing educational material, contracts, records, medical files, and even financial reports to be easily accessible to multilingual readers. Large international businesses or companies with multilingual employees often require corporate translation services.
- Technical Translation: Technical translations are ideal for translating complex ideas and concepts, primarily instructional content. Unlike corporate translations, though, technical translations use industry-specific terminology that the average translator may not know of. Manuals for heavy machinery like cars, construction equipment, and medical equipment require precise industry knowledge while being translated.
- Scientific Translation: Similar to technical translation, scientific translation uses field-specific terminology unique to different fields of study. However, this field of translation focuses on translating medical content, scientific records, academic papers, and other important informational content. Companies may require scientific translation services to properly translate an employee’s medical records or prescriptions.
What is Transcreation?
Transcreation is a step above translation in that it recreates the source material to fit a specific target audience’s language, cultural norms, and memetics. Unlike translation, transcreation involves a lot of creative writing on the translator’s behalf, mainly because the transcreator must adapt the work to fit a new culture while retaining the original work’s tone and intent.
How is Transcreation Different from Translation?
While transcreation and translation (specifically free translation) are similar, the key difference is in the amount of creative liberty the translators are given. For starters, some names, phrases, or cultural norms don’t have the same meaning in one culture or another. For example, the phrase “no va” means “doesn’t go” in Spanish, but we may associate it with the car brand Nova or the astrological phenomenon in English.
The Three Elements of Transcreation
According to linguist Mar Díaz-Millón, three elements make up a transcreation:
- Linguistic Translation is when linguists translate the source material directly into the target language.
- Cultural Adaptation is when linguists consult subject matter experts to ensure that their content will make sense and resonate with the target audience.
- Re-creation involves rewriting parts of the text to fit the original’s story beats, tone, and emotional intent.
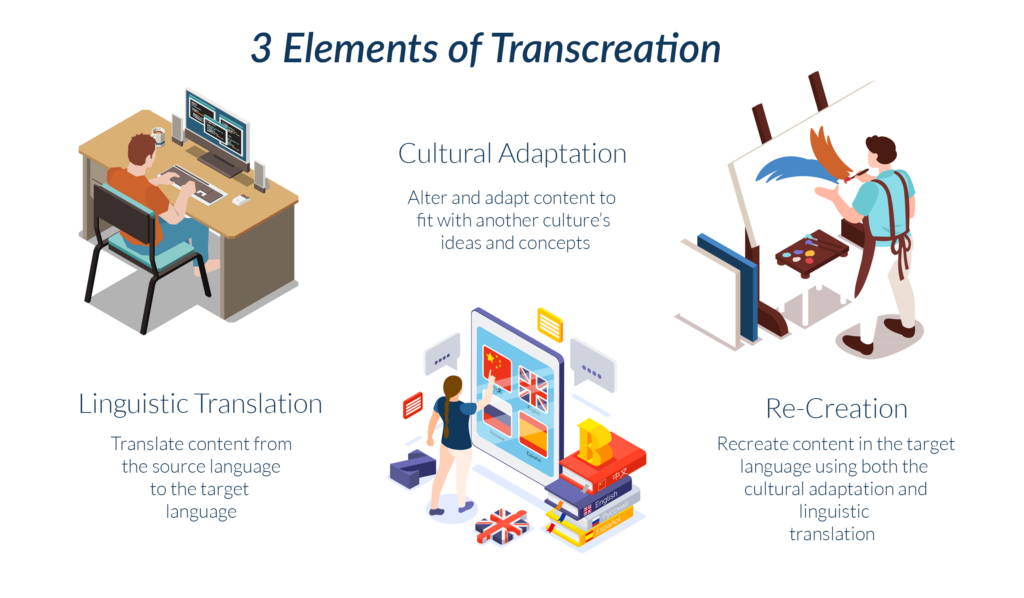
Transcreation Examples
So, what are some examples of transcreation?
Transcreation in Art: Examples
If you’ve ever watched anime or played a video game, you’ve seen transcreation in action. These art forms, which rely heavily on storytelling and visuals, utilize transcreation to spread a message, share a story, or evoke a specific emotion. Games like the Pokémon franchise use transcreation to give younger audiences an easier understanding of the game’s mechanics. Movies like The Ring utilize transcreation to create relatability and instill stronger emotions within the audience.
Transcreation in Literature: Examples
When it comes to literature, tons of stories have been transcreated over the ages to reach vast audiences. Classic or ancient literature, like The Epic of Gilgamesh or Don Quixote, use transcreation for archival purposes to continue to exist as educational tools and cultural artifacts. On the other hand, popular literature, comics, and children’s stories are also transcreated commercially to reach wider audiences. For example, books like the Percy Jackson Series and comics like The Sandman are translated into many different languages and scripts for readers everywhere to enjoy.
What is Localization?
Localization is the process of adapting different parts of a source work to fit another culture’s conventions. Localization may involve changing spellings, imagery, or specific phrases and actions to make more sense to the target audience.
What is the Difference Between Localization and Translation?
Localization is a process taken after translation; once a work is translated or transcreated into the target language, localization services reformat the work to fit the semantics of the target language. For example, your current computer operating system uses a 24-hour or 12-hour clock as the default, depending on your location.
Localization Examples
Localization happens constantly, and we often don’t even realize it. Here are some examples of localization that we encounter every day:
Localization in Art: Examples
In art, it’s a bit easier to tell when something’s been localized. For example, video games undergo localization processes all the time. The user interface, text scrolling, and even how certain items look are all subject to change during the localization process.
Localization Industry Examples
Another excellent example of localization is the Arabic packaging of 7-Up. From a distance, the logo on the soda looks the same as the English version. However, since the text is in Arabic, the logo designers had to reformat the text a bit to display the brand name correctly. As a result, the Arabic 7-Up logo has the word “up” in front of the number seven.

What are the Elements of Localization?
When it comes to localizing content, there are several elements involved, including:
- Text: During localization, some phrases and spellings may need to change for the text to make sense to the target audience. For example, the word “realtor” in American English means the same thing as “letting agent” in British English.
- Layout: As mentioned in our digital clock example, a program’s user interface may need slight changes depending on the target culture.
- Graphics and Multimedia: Visual content like advertisements, posters, and even food items are also subject to change in localization.
- Fonts: When localizing content in a different script (say, translating something from Japanese to English), font design may also be subject to minor changes to create a sense of unity between both versions of a work. For example, the Mr. Saturn font in EarthBound has a localized Engish version that evokes the same playful style as its original Japanese counterpart.
- Packaging: Depending on a country’s packaging requirements and labeling, your favorite chip brand may look different worldwide. Like the 7-Up example, packaging localization utilizes adapted logos, different fonts, and different labeling.
What is the Difference Between Translation, Localization, and Transcreation?
With a complete understanding of translation, localization, and transcreation, it’s time to review their differences.
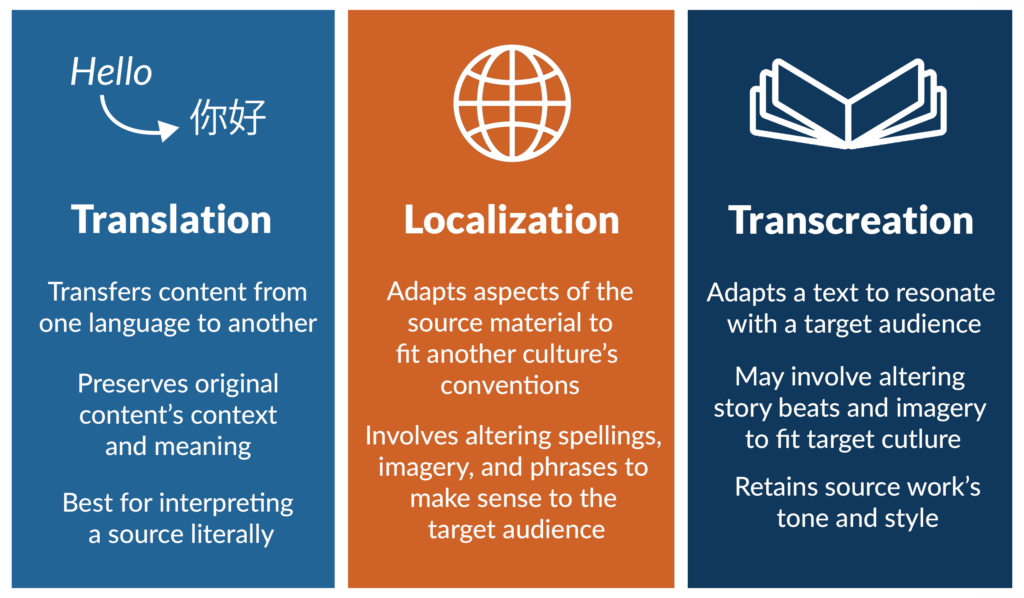
To start, translation is the process of turning content from one language into another language. It can sometimes include literal, word-for-word translations, but most involve minor changes to help the text flow naturally.
Both localization and transcreation take this initial translation and elevate it, changing content to make the translation better fit the target language’s cultural norms. However, unlike localization, transcreation further adapts a work to fit in with the target culture almost perfectly.
Transcreation vs. Localization: Purpose
Transcreation and localization also differ in purpose:
What is the Purpose of Localization?
To start, the purpose of localization is to modify content to fit the target audience’s language and preferences. Localization includes changing digital clocks, the direction text scrolls in a video game, changing b-roll audio, fonts, or signage to fit the target culture’s language, accents, and symbols.
Does Localization Include Translation?
Localization doesn’t always include translation. For instance, localizing software for the UK and the US doesn’t involve translation. Still, it does involve reformatting digital clocks from 24 to 12 hours and changing spellings from British versions to American ones. However, localization does play a significant role in international media, especially with cartoons and video games. In these situations, localization is a process that accompanies translation.
What is the Purpose of Transcreation?
Unlike localization, transcreation aims to translate a work’s tone, meaning, and emotional weight to a target audience. While this may include some aspects of localization, transcreation emphasizes altering aspects of the source material’s narrative to better suit a target audience. This may include massive changes, like altering character names or a story’s setting, or smaller changes, like altering how characters interact with each other to fit the target culture’s social norms.
Does Transcreation Include Translation?
In most cases, transcreation includes translation. After all, the first element of transcreation, linguistic translation, is necessary for an effective transcreation that retains the spirit of its source material.
Transliteration
Sometimes, translated, localized, or transcreated media also utilizes transliteration—a process that allows audiences in a target language to understand the names and pronunciations of locations, objects, food, and people.
What is Transliteration?
Transliteration is the translation of words between writing systems. While many languages use the Latin writing system, others, like Russian, Chinese, and Arabic, use different writing systems. Learning a new writing system can be especially difficult for people who don’t speak these languages, especially if it’s only for specific names and words. Transliteration aims to remedy this by rewriting words from one language’s writing system to another in a process called transliteration. The transliterated words will have the same pronunciation as they would in their source language, but their spelling will be altered to follow the phonetic conventions of the target language.

What is an Example of Transliteration?
Transliteration is everywhere. If you’ve ever ordered Chinese food, you’ve seen transliteration at work on the menu for food items like Lo Mein or Peking Duck. If you’ve watched anime or played a role-playing game, character names are often transliterated to stay faithful to the source material. In dictionaries, spellings of each word in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) exist below the defined word as a guide for teaching people how to pronounce it.
Transliteration vs. Localization vs. Transcreation
So, when it comes to transliteration, localization, and transcreation, what’s the big difference? All three are connected via shared processes and used in tandem with one another when handling international media and marketing.
What is the Difference Between Transcreation and Transliteration?
The biggest difference between transcreation and transliteration is their use. Transcreation often involves changing character, location, and food names to better fit the target language’s audience. Transliteration, however, aims to preserve the source language’s original names and pronunciations instead of writing them out in a different script so readers and audiences can understand and pronounce the word in question. In many cases, transcreation and transliteration provide a culturally accurate and easy-to-understand version of the source material for non-native speakers.
What is the Difference Between Transliteration and Localization?
Regarding localization, the major difference between transliteration and localization is their methodology. While transliteration rewrites content to fit the target language’s phonetics and writing system, localization reformats content to make it easier for audiences to interpret based on cultural norms.
Have a Project in Mind?
Are you unsure whether or not your project needs translation, localization, or transcreation services? Don’t worry; we’re here to help. Schedule a consultation with us today to help find the perfect fit for your project. Then, use our new platform to browse, match with, and communicate with your translators all in one place. To learn more, sign up here.
We look forward to working with you!





0 Comments