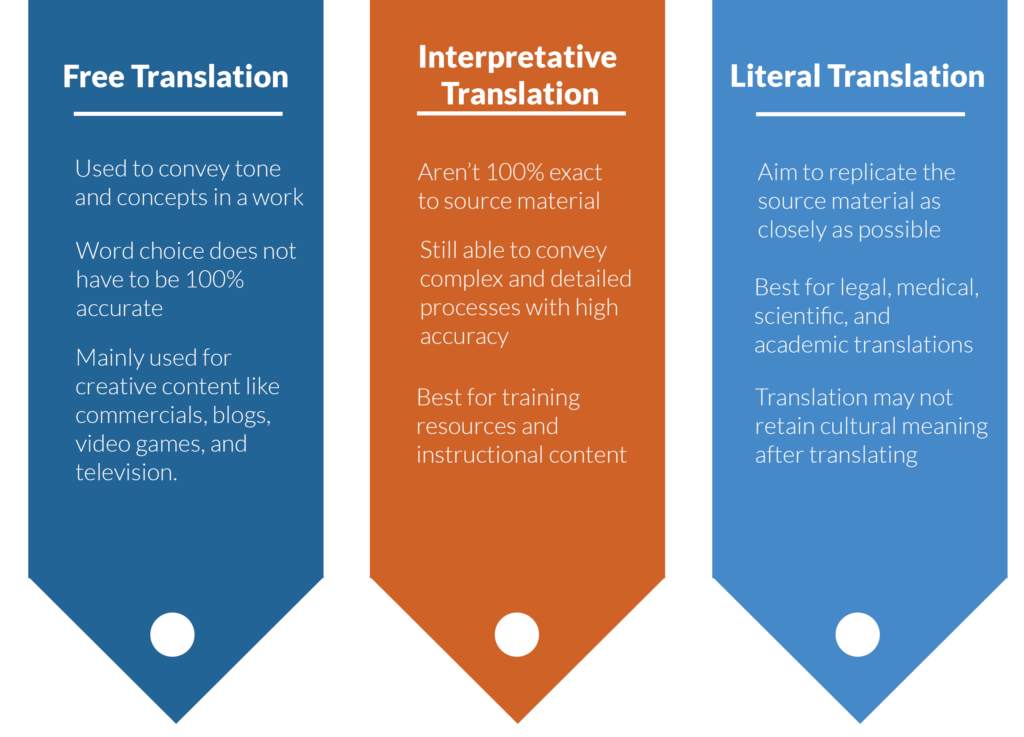
- Literal Translations ensure that all translated info is as close to the source material as possible, sometimes too much. Seasoned experts often use literal translation for technical content such as engineering, scientific, or specialized medical documents. Amateur translators tend to apply this technique instinctively to everything they translate, making their translations sound robotic, sometimes even forcing translation mistakes on their content.
- Interpretative Translations accurately translate complex ideas and instructions to the target language. The ability to interpret the source text and convey the message to the target language while avoiding literal translation is a skill acquired with years of practice.
- Free Translations aim to convey the source material’s original message using completely different words in the target language. It’s a creative technique often used in literature, promotional content, or when translating slang.
Sometimes, though, translators can’t convey the same tone in a free translation that the source material has. Perhaps a common phrase doesn’t translate into the target language, or the source material references something well-known in their specific culture that international audiences won’t understand. That’s where transcreation comes in.
What is Transcreation?
Transcreation is the process of translating a work and then adapting it to suit the target language’s audience as closely as possible. Consider it a step further than translation; translations aim to replicate the source material using equivalent words in the target language. In contrast, transcreations aim to replicate the source material’s tone and intent while making it easily understandable for audiences from different cultural backgrounds. In some instances, a transcreator may completely change translated words to the point where they won’t make sense when translated back into the source language. However, to native speakers, the new text retains the same tone and meaning as the source text.
What are the Types of Transcreation?
Transcreation has its uses in a variety of fields, especially those that rely on delivering emotional messages and maintaining a specific tone throughout. Some of the most popular types of transcreation include:
- Marketing Transcreation: Like marketing translation, marketing transcreation aims for accuracy while maintaining a brand’s voice and message.
- Business Transcreation: Business Transcreation handles corporate materials like emails, general updates, and internal communications.
- Literary transcreation aims to convey the tone and plot of a story as accurately as possible, as well as the original writer’s intent. For works like poems and songs, transcreators must also aim to maintain a similar meter and rhyme scheme.
What are the Three Elements of Transcreation?
There are three main elements of the transcreation process:
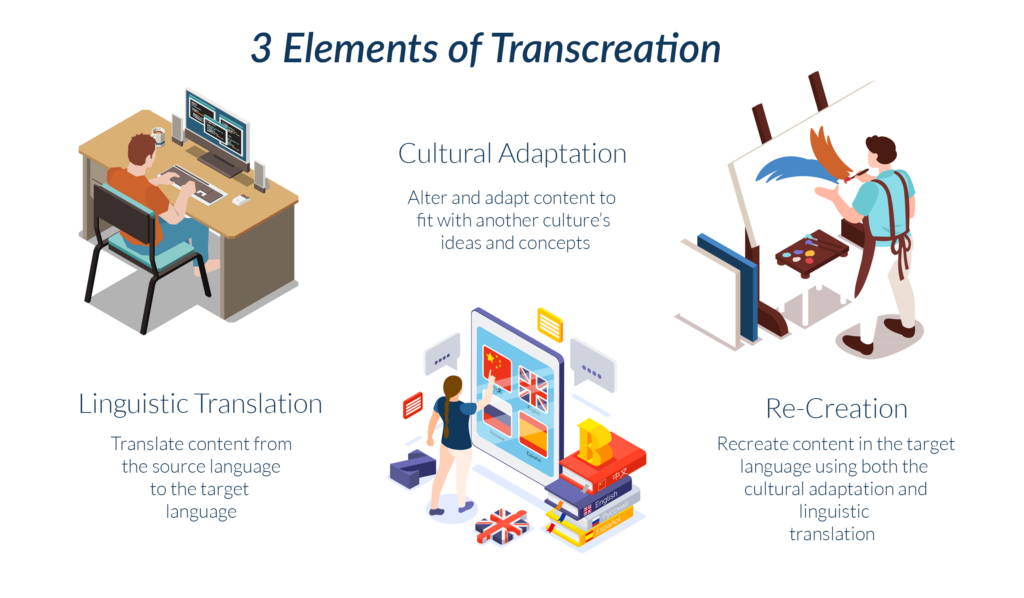
Linguistic Translation
As the first step of the process, linguistic translation involves translating the source material into the target language.
Cultural Adaptation
This next step involves adapting the material to suit your target audience. Adaptations could involve changing sign text to your target language, replacing food items with ones commonly seen in that culture, or altering terms and phrases to better fit the target audience’s memetics.
Re-Creation
Sometimes called re-interpretation, the re-creation element involves reimagining the source material that combines linguistic translation and cultural adaptations to create a piece that stays true to the source material while remaining accessible to international audiences.
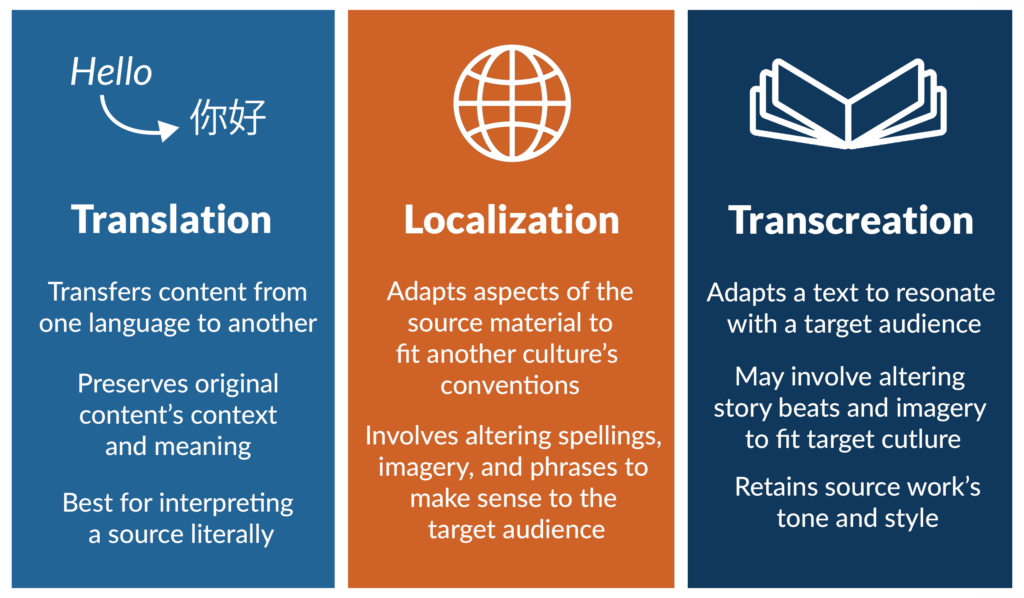
Transcreation Vs. Translation
So, with all the talk of translation in transcreation, what’s the difference between the two?
Building Upon Translations
Generally speaking, creative liberty is the main difference between transcreation and translation. Translations focus on accurately converting text from one language to another; transcreations build upon that to create a deeper cultural meaning. Thus, transcreators usually have more creative liberty while working on a project.
Is Transcreation a Translation?
So, this begs the question: Is a transcreation a translation? While the two are different, translation is essential in developing a transcreation. After all, staying true to a message’s original intent is still important!
Think of it like this: a translation is like watching a subtitled film. The script hasn’t been changed, and everything the actors say on screen is relatively accurate to the original film. A transcreation is like watching a dubbed and localized version of the same film— it’s still, in essence, the same movie— but phrases, locations, and background items might be different from the original version.
Transcreation vs. Transliteration
Sometimes, specific words, phrases, or place names can’t be translated into another language, and transcreating them isn’t a viable option. What happens then? Transliteration.
Transliteration plays a significant role in the development and adaptation of media. Although it’s not nearly as prevalent as translation and transcreation, this process is everywhere, and just like translation and transcreation, you may experience transliteration without even realizing it.
What is Transliteration?
Transliteration is the phonetic translation of words. Many different languages have different writing systems attributed to them, and these writing systems all share the same function: to associate letters and symbols with phonetic sounds used in spoken language. When sharing these words with other cultures, linguists must produce methods for non-native speakers to read and interpret the other language’s sounds accurately. So, instead of writing the word “cat” in Arabic script (قط), linguists would write the pronunciation using Latin letters (qut).

Transliteration and Translation
It’s essential to keep in mind that transliterations aren’t translations. While they’re often used in translated works (think character names in an anime), they aren’t translations of the word itself. They are linguistic representations of these words using another script.
A universal example of transliteration is with the phonetic alphabet, which you’ll find most often in dictionaries. The phonetic alphabet uses a variety of symbols to represent every possible sound (phoneme) in a language. To write out the pronunciation of a word, linguists will use the phonetic alphabet to represent sounds. For example, the word “cat” in the international phonetic alphabet would be spelled “kæt.”
Why is Transliteration Important?
Transliteration plays a vital role in how we share languages. Whether comparing and contrasting our different words for “cat” or learning how to pronounce names and places from around the world, transliteration gives us the tools to learn new languages with what we already have.
Transcreation Examples
Sometimes, we know that a piece of art or media has been translated and localized, but most of the time, we take in transcreated content without even realizing it. Since the industry plays a role in content creation, marketing, business, and art, you can find examples of transcreated content almost anywhere. Here are some examples:
Transcreation in Marketing
When it comes to marketing translation and transcreation in the marketing industry, you’ll find most examples in the form of international ad campaigns. Whether it’s a website, a billboard, or a product’s packaging, marketing transcreators are behind the slogans, copywriting, and catchy phrases, transcreators work to carry over a brand’s specific tone and intent.
Transcreation Online
In the digital space, websites with international audiences must maintain a consistent tone of voice regardless of the language in which the user is accessing the website. Social media platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and (formerly) Twitter are great examples of sites with lots of international traffic that require many different types of translation to function correctly.
Transcreation in Packaging
Popular international foods will also feature transcreated content in their packaging. For example, the popular candy Pocky isn’t packaged in Japanese for everyone— it has to be written in other languages for international sale. The same goes for Coca-Cola and PepsiCo products as well: not only do these products require appropriate labeling, but they also need to be accessible for buyers to read. So why not just transcreate the whole product?
Transcreation in Advertising
Slogans play a significant role in more than just packaging. They also give consumers a specific emotional tone to associate with the brand and product. You’ll always see slogans on packaging, on the internet, and in physical ads. For international businesses, these slogans must remain consistent between all languages. Otherwise, you get KFC’s 1980s blunder: “Eat your fingers off.”
What is Transcreation in Art?
In art, transcreation is the primary way we share artwork and creative concepts with international audiences. If you’ve played a video game, watched a dubbed movie, or read a piece of ancient literature, you’ve already experienced transcreation in art. Here are some more examples of transcreation in the art world:
Transcreation in Literature
Popular book franchises like Harry Potter and The Hobbit are often transcreated into many languages for different audiences. In fantasy settings like these, transcreators must also rename creatures, spells, and places to fit an audience’s understanding and pronunciations while maintaining the original work’s tone.
Ancient texts like The Epic of Gilgamesh are also transcreated into modern languages. While these projects usually take part in museum and archival spaces, translating and interpreting dead languages is also essential to conservation. Depending on which museum translates a work, you may get different-sounding texts entirely!
Transcreation in Music
In music and poetry, transcreators need to go the extra mile to ensure a song or poem retains its rhyme scheme, rhythm, and meter on top of its tone. One of the most famous transcreations of a song, the Spanish version of Bon Jovi’s This Ain’t a Love Song, does just that.
Transcreation in Film
The film industry holds a massive market for transcreation. After all, who doesn’t love movies? When filmmakers transcreate their works, it’s more than just translating the script too: some scenes may require different props to make the script work, or signage in the background may need translating too. Most of the time, you’ll see these minor changes in animated films and television, like Disney movies, anime, and other cartoons.
Transcreation in Video Games
In video games, transcreation best practices look a lot like the ones for a film. Since video games are an interactive visual medium, the game’s script, environments, signage, and even items will need alterations to best resonate with other audiences. A great example of transcreation in video games is the Pikmin series, where items resemble popular products and brands from that particular culture.
Transcreation Rate Per Word
So how much do transcreations cost? Generally speaking, transcreations cost more than translations since they require extra time and effort to produce. However, rates for transcreations and translations will vary depending on the translator, the type of content being translated, and other related factors.
In addition, transcreators have different skill sets than their translator counterparts. While translators need to be experts in the languages they work with, transcreators need experience in storytelling and the ins and outs of the cultures they’re working with. You’ll often see translators and transcreators working as a team since both skill sets are essential to effective localization.
How Do You Pay for a Transcreation?
It’s important also to remember that, unlike translators, many transcreators rely on hourly rates instead of charging per word. Hourly rates tend to change based on the breadth and scope of the project and what the client can afford— don’t be afraid to ask about rates!
Why do Transcreators Get Paid Hourly?
Transcreators often use hourly rates to compensate for the extra time spent adapting content to best suit the target language’s cultural context. During the transcreation process, transcreators often have to add or change aspects of the text to be understandable to the target audience. While they aren’t necessarily working directly with words, they still work on the project and should be compensated fairly.
Looking for Transcreators?
Ready to get started on your next translation or transcreation project? Traduality has everything you need to succeed; create your first project today and find vetted translators, or book a meeting with us to learn more about your specific needs.





0 Comments