The translation industry is massive and involves nearly every aspect of our lives. In such a diverse, globalized society, it has to overcome language barriers, share ideas, and keep people informed. With such a wide range of industries and content to cover, the term “translation” can’t perfectly cover every aspect of the process. So, what are the different types of translation, and how do they differ?
What is Translation?
Before getting into the different types of translation, it’s important to understand what translation is in the first place.
Translation is when linguists transfer text from one language to another. Translators typically specialize in a few different languages and need complete mastery over them. They also tend to have experience in specific fields of study and translation types.
What are the Three Types of Translation?
There are several ways professionals categorize the translation process when it comes to different kinds of translation. The first method uses three types of translation, each varying based on the translation’s complexity:
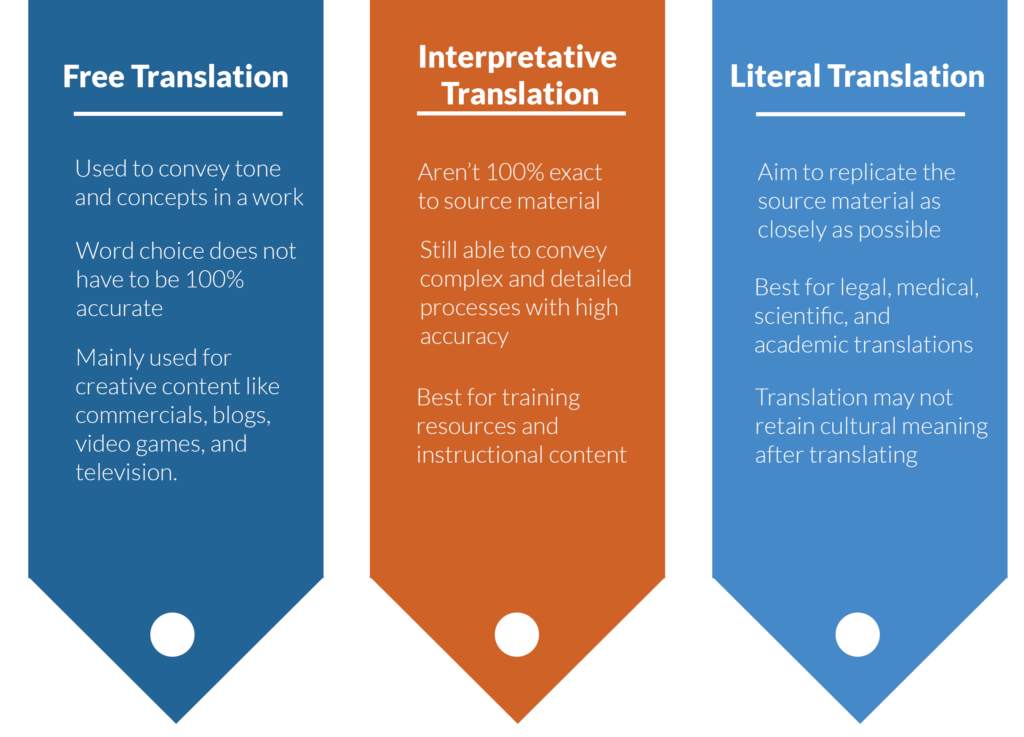
Literal Translation
Literal translations are as close to the source material as you can get. These translations aim to replicate the source text word-for-word or as close to word-for-word as possible while remaining grammatically correct. Literal translations are best used for legal and medical documents, requiring highly specific terminology to convey information accurately.
Interpretative Translation
Interpretative translations are the next degree away in likeness to the source material. These translations aim to stay as close to the source text as possible but often involve minor changes to make the content more accessible to target audiences. These changes include altering common phrases and memetics or changing numeric values through localization. Interpretative translations are best for educational materials that relay complex information but don’t require precise terminology like legal or medical translations.
Free Translation
Free translations are the third degree away from the source material. Like interpretative and literal translations, free translations aim to replicate certain aspects of the source material. Instead of conveying complex instructions or using specific terminology, free translations aim to convey the source material’s tone and message. These translations are ideal for creative works, where emotional weight matters most.
What are the Four Types of Translation?
Another way professionals categorize translation is through the different ways it’s used. The four types of translation emphasize these industry differences:
Creative Translation
Creative translation isn’t just for movies, books, and video games (although they are covered under the creative translation umbrella). Creative translation also includes translating marketing materials, including packaging labels, iconography, web copy, SEO keywords, and other promotional materials.
Corporate Translation
Corporate translation revolves around translating key documents that businesses need to run smoothly. Employee manuals, customer-facing educational material, contracts, records, medical files, and even financial reports are essential for any business and must be translated accordingly.
Technical Translation
Technical translation is the fourth of the primary types of translation, and it is mainly used for educational materials that involve strict technical terms and complex ideas. Instruction manuals and safety guides require technical translation services.
Scientific Translation
Like technical translation, scientific translation uses field-specific terminology unique to different studies. However, scientific translation doesn’t always include translating equipment manuals and instructional content. Instead, the realm of scientific translation covers other kinds of specialized content. Medical content like prescriptions, test results, patient records, and informational pamphlets need scientific translation, as do scientific research papers and studies.
What are the Five Types of Translation?
In addition to the four types of translation, there are several other ways to classify translation based on industry and purpose. Generally speaking, we can classify translation in many different ways based on the industries each service participates in. Five common industries include:
- Marketing Translation involves translating commercial content.
- Literary translation involves translating books and other literary materials.
- Website Translation involves translating web copy and web content.
- Medical translation involves translating medical materials, like medical documents, patient records, and informative content.
- Legal translation involves translating materials used in court, like court transcripts, witness testimonies, and legal documents like contracts.
What are the Eight Types of Translation?
To expand on these industry-specific translations further, here are eight more types of translation based on industry:
- Software Localization involves translating and localizing computer software for international users.
- Scientific translation involves translating scientific materials, including research papers and studies.
- Document Translation involves translating important documents, like birth certificates and driver’s licenses.
- Financial translation involves translating financial documents like bank statements and loan information.
- Video Game Translation involves translating and localizing video game content.
- Film Translation involves translating movie and television scripts for international audiences.
- Multimedia Translation involves translating mixed-media artwork for audiences to understand.
- Academic translation involves translating educational materials, academic papers, and even archival materials for preservation.
Other Types of Translation
Russian-American linguist Roman Jakobson also classified different types of translation based on their processes:
Intralingual Translation
Jakobson’s first type of translation, intralingual translation, involves translations that occur within the same language.
What is Intralingual Translation?
Paraphrasing, rewording, and reformulating sentences are all part of the intralingual translation process. In many cases, translators implement intralingual translation alongside the other types of translation Jakobson describes since word-for-word translations aren’t always grammatically correct to begin with.
Examples of Intralingual Translation
If you’ve ever paraphrased a quote for a research paper, you’ve encountered intralingual translation in its purest form. Other examples of intralingual translation include explaining highly specific words in layman’s terms for general audiences to understand and altering spellings or phrasing to fit a particular dialect.
Interlingual Translation
Interlingual translation involves translating content from one language to another.
What is Interlingual Translation?
Interlingual translation is the form of translation most people are familiar with. Translating text or spoken content from one language to another makes it accessible to a broader audience.
Interlingual Translation Examples
You’ll find interlingual translation almost everywhere: on Netflix, in books, advertisements, and websites. In today’s globalized world, media distribution isn’t necessarily tied to a single location. The internet has made intralingual translation more relevant than ever.
Intersemiotic Translation
Jakobson’s third type of translation, intersemiotic translation, often combines interlingual and intralingual.
What is Intersemiotic Translation?
Intersemiotic translation involves the adaptation of a source material into another medium. Since the translation process involves altering a work to fit the target medium, intralingual translation is also involved to ensure that the adaptation flows smoothly.
Intersemiotic Translation Examples
Movie adaptations are by far the most well-known example of intersemiotic translation. Films based on books, comics, and even video games are all types of intersemiotic translations: they require extensive knowledge of the source material and the new medium the source material will be adapted for.
Types of Translation and Interpretation
In addition to Jakobson’s different types of translation, there are also different types of live translation or interpretation, classified by the interpreter’s presence and how they work alongside the speaker to interpret content.
Simultaneous Interpretation
With simultaneous interpretation, the speaker and the interpreter talk simultaneously. This form of interpreting is the most common for American Sign Language.
Consecutive Interpretation
During consecutive interpretation, the interpreter speaks after the speaker finishes their thought, sentence, or presentation.
In-Person Interpreting
If the interpreter is present at an event and works alongside the speaker physically, they’re interpreting in person.
Remote Interpreting
If the interpreter is not present at the event and uses a phone, the internet, or a voice recording, they are interpreting remotely.
What are the Three Types of Localization?
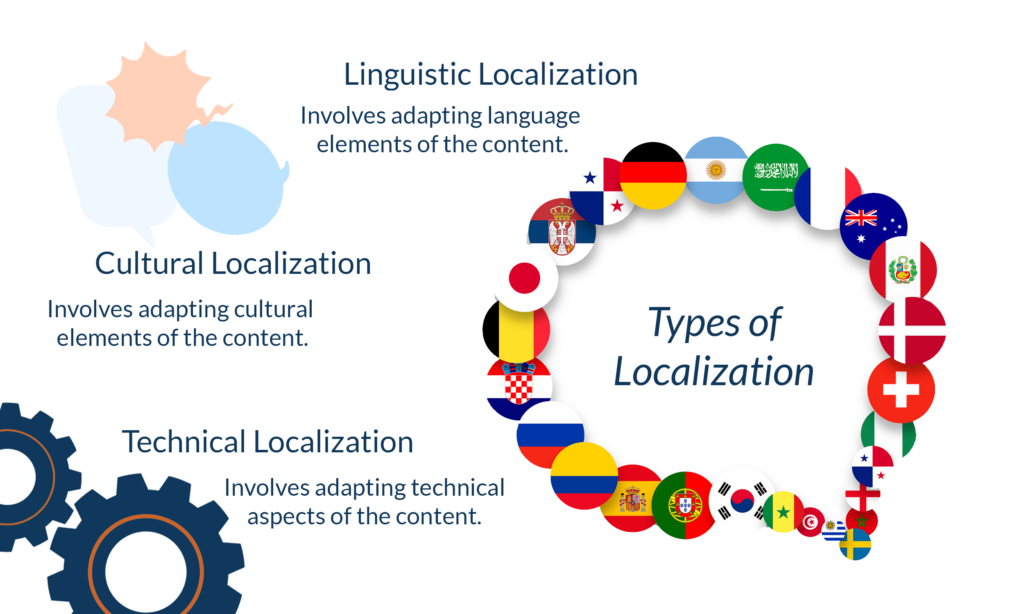
In addition to the types of translation, there are also different types of localization. Since the localization process and translation process often go hand-in-hand, these techniques are often used alongside the different types of translation:
Linguistic Localization
Linguistic localization involves adapting the language elements of a work. Linguistic localization involves not just translation but adapting idioms, slang terms, and cultural references to make sense to the target audience. In addition, linguistic localization may involve changing the spellings of certain words to fit a particular dialect. For example, British English uses terms and spellings that are different from American English, and localization teams must create two versions of their product to fit both conventions.
Cultural Localization
Cultural localization involves adapting cultural and sociological elements of a work. In cultural localization, the localization team might change symbols, color schemes, and even the product’s user interface to better fit the target culture’s conventions and cultural norms. An easy-to-spot example of cultural localization exists in the Spirit Temple in Ocarina of Time for the Nintendo 64: the pushable blocks in the original Japanese version have a different symbol than in the English version.
Technical Localization
The technical localization process involves changing a work’s formatting: currencies, time and date formats, and keyboard layouts are all subject to change with technical localization. For example, your computer’s operating system will have different date and time formats based on the location you input when setting up your computer.
Translation Techniques
Regarding how translators do their job, there are different types of translation techniques that translators employ:
What are the Types of Translation Techniques?
Generally, translation techniques can be divided into two categories:
Human Translation
Human translation is traditional translation; a human linguist translates content from one language to another. This technique doesn’t involve any AI or computer elements besides the necessary programs to manage projects and type out translations.
Machine Translation
Machine translation, on the other hand, utilizes AI or large language models (LLMs) to create translations faster than human translation does. However, the downside to this technique is that machine translations are largely inaccurate—AI cannot account for specific tonal shifts or cultural meanings that are so heavily prevalent in language.
Machine Translation with Post Editing
To provide more accuracy and create translations that make sense both culturally and grammatically, post-editing techniques have become increasingly popular in the machine translation space. These techniques utilize a mix of human and machine translation: an LLM completes the first draft of a translation, and human translators edit the text to create a more accurate version.
Translation Tools
So, what translation tools are available for the average person to use?
Online Translation Tools
Generally speaking, the best place to find translation tools is online. As the primary way of connecting us to the global world, the internet has tons of resources for translators and people needing translation services. The realm of online translation tools is vast and varied. While some online resources include translation agencies and marketplaces, others include LLMs and AI translation tools.
AI Translation
AI Translation is a type of machine translation that utilizes artificial intelligence to translate content without the need for human involvement. Programs like Google Translate, for example, use a complex large language model to translate words between languages instantaneously. However, AI translation isn’t the best tool for translating longer pieces of content. AI translations typically lack the cultural nuance that human translations have, and while they’re great in a pinch, they aren’t the best.
To help improve the accuracy of an AI translation, clients can select AI translation services with human post-editing to ensure their translations are accurate.
CAT Tools
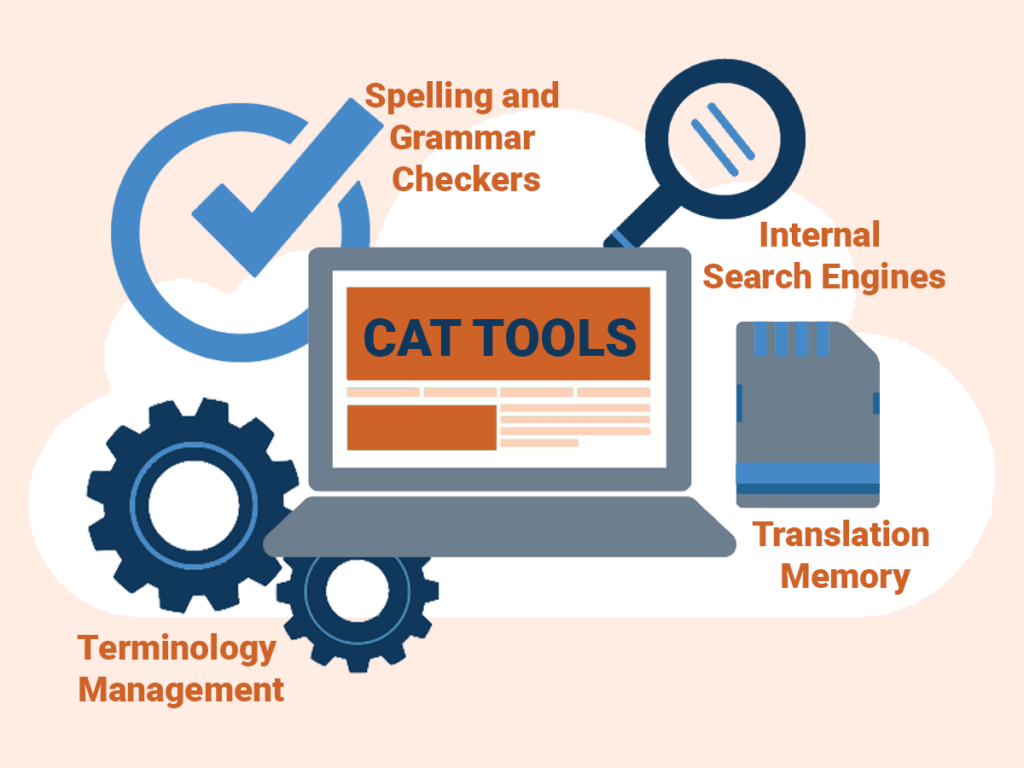
Computer-assisted translation tools (CAT tools) aid translators by taking the busy work out of translation. Translators can use CAT tools to access a client’s translation memory, manage essential terminology for a project, and automatically check translated documents for consistency, spelling, and grammar. Like Google Docs or Microsoft Word for writing, CAT tools don’t translate content; they make it easier for the translator to do their job.
Translation Agencies and Marketplaces
If you’ve got a translation project but aren’t sure where to get quality translation services, translation agencies and marketplaces are here to help. These organizations help clients find specialized translators and provide translators with clients. Translation marketplaces like Traduality also offer a platform for freelance translators and provide project management services in-app to streamline the translation process.
Need Help With a Project?
Ready to get started on your next translation project? Traduality has everything you need to succeed; create your first project today and find vetted translators, or book a meeting with us to learn more about your specific needs.





0 Comments