In today’s globalized world, businesses constantly seek to expand their reach beyond borders. However, entering a new market involves more than just translating your website or product information; it requires a comprehensive approach known as localization. This process is crucial for adapting your product or service to meet a local audience’s specific needs and preferences. But did you know that there are different types of localization? In this article, we will explore the three main types of localization and delve into various aspects such as language localization, localization strategy, and more.
What is Localization in Translation?
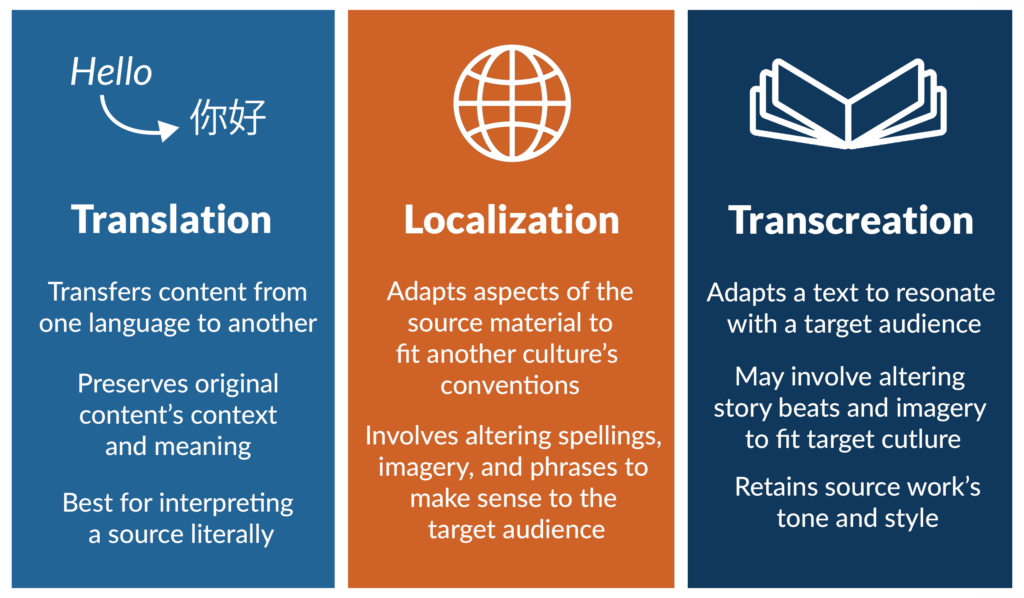
In linguistics, localization refers to adapting language to fit a specific region’s cultural and social norms. It involves adapting the language elements of a product or service. This includes not just the translation of text but also the adaptation of idioms, slang, and cultural references to make the content relatable to the target audience. While it may seem similar to transcreation, the two have specific differences. We won’t go into detail here, but you can find more information in our article on Transcreation vs. Localization.
What are the Three Types of Localization?
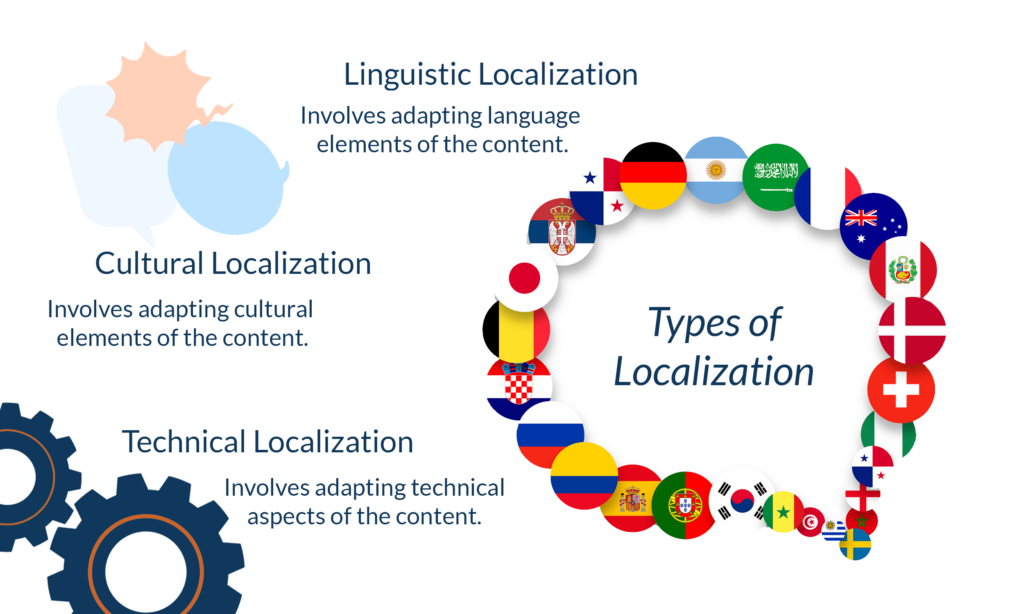
Localization can be broadly categorized into three types: linguistic, cultural, and technical. Each type serves a unique purpose and is crucial for successfully adapting a product or service to a new market. Let’s explore them:
- Linguistic Localization: This involves adapting the language elements of a product, service, or content. It’s not just about translating text; it also includes adapting idioms, slang, and cultural references to make the content relatable to the target audience.
- Cultural Localization: This type of localization focuses on adapting the cultural elements of a product or service. This could include changing colors, symbols, and even the user interface to better suit the cultural norms and expectations of the target market.
- Technical Localization: This involves adapting the technical aspects of a product or service to meet the specific needs of a local market. This could include changing the currency, date formats, or even keyboard layouts to align with local standards and preferences.
Localization Strategy
The localization strategy involves adapting a product or content to fit a target market’s linguistic, cultural, and technical requirements. Key elements include linguistic adaptation, visual adjustments, technical modifications, functional compatibility, legal compliance, cultural sensitivity, and marketing considerations. The strategy also involves quality assurance and project management aspects like timeline and budget planning. Overall, a well-executed localization strategy ensures that the product resonates with local audiences, complies with regulations, and meets quality standards. To do so, it is highly recommended to do market research to identify local needs, hire local experts for cultural adaptation, and use local languages for customer service.
Advantages of Localization
Localization offers the advantage of making a product or service more accessible and appealing to a local market, thereby increasing sales and customer engagement.
Localization Team
A localization team is essential for adapting a product or content to a specific market’s language and culture. The team typically includes translators, editors, project managers, and quality assurance testers. Translators handle language nuances, editors focus on context, project managers oversee timelines, and testers ensure the end product meets quality standards. Together, they ensure the product is linguistically accurate and culturally relevant, enhancing its appeal and usability in the target market. There are two keys to achieving it:
Guidelines
Localization guidelines help adapt a product or content for a specific market. They cover language nuances, cultural sensitivity, technical requirements, legal compliance, and visual elements. These guidelines also outline procedures for quality assurance, functional testing, project management, and feedback collection. They aim to ensure consistency, quality, and cultural relevance during the localization process.
Quality Assurance
Localization Quality Assurance (LQA) involves checking the quality of translated or localized content to ensure linguistic accuracy, cultural relevance, and technical functionality. It combines automated tools and manual reviews to identify and fix errors, aiming for a seamless user experience across different languages and regions.
What are Examples of Localization in Business?
In business, localization can involve adapting marketing materials, product packaging, and even the product itself to meet the needs and expectations of a local market. Here are some examples:
- Website Localization: Companies like Amazon customize their websites to offer multiple languages and currencies based on the user’s location. This makes the online shopping experience more user-friendly for a global audience.
- Cultural Sensitivity in Marketing: Coca-Cola adapts its marketing campaigns to align with local holidays, traditions, and idioms. This ensures the brand resonates with the local audience and doesn’t inadvertently offend cultural sensibilities.
- Legal Compliance: Streaming services like Spotify and Netflix have to comply with local laws regarding content ratings and censorship.
- Social Media Localization: Brands often have separate social media pages for different countries to post relevant content to that specific audience.
Each of these examples highlights how businesses modify various aspects of their operations to better suit the needs and preferences of local markets.
As you may notice, localization is not a one-size-fits-all process; it involves various types and elements that cater to different needs. Whether it’s language, content, or UI/UX, understanding the different types of localization can help businesses make more informed decisions.
Ready to get started on your next translation project? Traduality has everything you need to succeed; create your first project today and find vetted translators, or book a meeting with us to learn more about your specific needs.
Updated 2/21/2024.





0 Comments